Health: Myths About Sunscreen.
Myths about sunscreen.
Often, we love going out to experience the fantastic feeling of the
sun's warmth. Going out is fun; it increases one's mood, harnesses improved
social interaction, provides access to enhanced air quality, and decreases
stress and anxiety. The body naturally produces vitamin D with the aid of
sunlight. Vitamin D reduces depression, strengthens bones, boosts the immune
system, lowers preterm labour risk, and improves sleep.
Although the sun produces vitamin
D, which is good for the skin, it is advisable to protect one's skin against
sun rays, UVA, and UVB exposure before you go outdoors. The protection can be
in the form of applying sunscreens, as health practitioners recommend. Apart
from sunscreens, attires that cover your neck, hands, and legs are encouraged
because they stop the rays from penetrating deep into your screen. The truth is
that failure to protect your skin from sun rays causes your skin to age
prematurely, and you risk contracting skin cancer. The danger might sound
false, but it is a reality we must not neglect.
There are myths and
misconceptions about sunscreen, but knowing the facts behind the sunscreen is
necessary towards using it correctly. Let us look at some of those myths:
All sunscreen is the
same.
Saying that all sunscreens are
the same is like claiming that all lakes are the same, an incorrect argument.
No sunscreen is the same, as each composition differs from the others. There
are different lakes, namely freshwater, saline, Rift Valley, and permanent and
temporary lakes. These lakes have different sizes, water volumes, and lengths
and cannot be the same.
Similarly, sunscreens cannot be
the same as there are two types: physical and chemical. Physical sunscreens use
the minerals zinc oxide or titanium dioxide to block UV rays from the skin,
like a shield. Contrarily, chemical sunscreens block UV rays using substances
like avobenzone, oxtinoxate, and oxybenzone.
Sunscreen reduces
vitamin D levels.
If sunscreen reduces vitamin D,
why not makeup and body lotions? Are they not smeared on the skin like
sunscreen? Why are they not blocking vitamin D like sunscreen, as some argue?
One source of vitamin D is
sunlight, which is present in some foods and supplements. However, there are
better ways to obtain enough of this vitamin than unprotected sun exposure, as
stated by Antony Young, PhD, a professor emeritus of experimental photobiology
at St. John's Institute of Dermatology in London. Anthony Young notes that a
small amount of UVB rays that get through sunscreen is enough to help your body
manufacture vitamin D. It is good to be aware that you can still acquire
vitamin D through diet and supplements rather than intentionally exposure to
harmful UV rays. Fatty fish, fortified orange juice, milk, egg yolks, beef
liver, and cheese are some foods high in vitamin D.
Any cloth blocks sun
rays.
Each cloth serves its purpose as
it insulates the body against cold or heat conditions, provides a hygienic
barrier, and keeps infectious and toxic materials away from the body. Then
there are specific clothes that protect the body from ultraviolet protection.
According to a study by the Skin Cancer Foundation, lighter hues like white and
pastels and darker or brighter shades like red, black, and navy blue absorb
more UV rays. Additionally, thicker, denser, and tighter weaves offer more
protection than thin, light, and loose fabrics. Furthermore, oversized clothes
protect your skin from harmful sun rays compared to smaller ones. The same also
applies to hats. The best caps for sun protection have a wide brim because they
are an excellent way to supplement daily sunscreen use in protecting your face
from Uv light, along with UV-filtering sunglasses. They can also help defend
forgettable areas like the tops of your ears and your scalp. Furthermore, less
restrictive clothing is more protective than extremely tight clothing! Too much
compression can stretch or tear fabric fibres, allowing more UV light to pass
through the garment.
People with
dark-coloured skin do not need sunscreen.
It would be best to avoid
overexposing yourself to the sun because of the misconception that people with
dark skin do not need sun rays. Despite having better sun protection, people
with darker skin should still use full-spectrum sunscreen. Some people hold the
opinion that those with darker skin types do not need to use sunscreen. This
belief .bbis due to melanin's ability to diffuse UVB rays and the potential for
partial sunburn protection. Melanin does not provide the same level of
protection from UVA damage, which can result in early ageing and wrinkles of
the skin. Everyone should wear sunscreen, regardless of skin tone, according to
the American Academy of Dermatology, because no matter your age, gender, or
race, skin cancer can affect you.
Sunscreens with Higher
SPFs give significantly more protection.
Always it is not the quantity but
the quality of something that proves its effectiveness. Shifting focus on
quality rather than quality to have proper priorities in life. Quality comes
with depth, is the best option, saves you energy, money, and time makes you
happy, and imparts you more knowledge. Sun Protection Factor (SPF) measures a
sunscreen's ability to prevent UVB rays from damaging the skin. Most people
believe that sunscreen with an SPF of 100 offers more than three times the
amount of sun protection as sunscreen with an SPF of 30. Ninety-seven per cent
of the sun's rays are blocked by sunscreen with an SPF of 30. While higher SPFs
are more expensive, they only stop 1 to 2 per cent more, and no sunscreen can
block 100 per cent.
Sunscreens are
waterproof.
Can one honestly argue that
sunscreen looks like plastic, rubber, wax, silicone, or later, that can keep
water out? There is nothing like waterproof sunscreen. While sunscreen brands
claim to be waterproof or water-resistant, no sunscreen is completely
waterproof. According to the US Food and Drug Administration, sunscreen cannot
claim to be waterproof and can only be waterproof for up to 80 minutes before
needing reapplication. Even then, all the sunscreen has to be reapplied after
two hours anyway, so it doesn't make much difference.
You do need to wear
sunscreen indoors.
We construct our houses in a way
that enables light to come in; no wonder every home has more than one
transparent window to allow in light. The windows could have been opaque or
absent if the light was not essential. Believing that sunlight does not have access
to your house is a self-deception. Apply sunscreen to all bare skin, even if
you spend most of your time indoors, especially if you're close to a window.
Window glass may block UVB rays but not UVA rays. According to studies,
prolonged exposure to UVA rays from windows can shorten the lifespan of the
skin by five to seven years and, more importantly, raise the risk of skin
cancer.
You do not need
sunscreen when it is cloudy or cold.
Clouds are not for blocking
visible light, not Ultraviolet rays; they only reduce them. During periods of
intense overcast, clouds can block up to 70% of these UV-B rays. The UV Index
is directly related to the amount of radiation received at a given time of day
and year. The reality is that you can get sun damage on windy, cloudy, and cool
days since UV radiation, not temperature, harms the skin from the sun.
Protecting your skin from the sun is still important, even if the weather is
not primarily sunny. Up to 90% of the sun's rays can reach your skin on cloudy
days. Sun damage is also possible on cloudy days because UV radiation can
sometimes pass through the clouds and may even be intensified by reflection on
them. When you are near water or sand, these elements reflect the sun, exposing
your skin to other indirect UV rays and increasing the risk of burning yourself.
You need to apply
sunscreen once a day.
Have you ever wondered why
breakfast, lunch and supper are essential to one's health? Why don't you wait
till the next day to eat another breakfast? You cannot wait for the next day
because it is the nature of the body to demand food after a particular period.
The same principle also applies to sunscreen. As its value depreciates with
time, you need to add more to keep it as effective as possible. Experts
indicate that sunlight breaks sunscreen down, so it's less effective as the day
goes by. To work optimally, reapply sunscreen every 2 hours or after swimming,
bathing, or excessive sweating. You may not need a second application if you
work indoors and sit away from windows.
Instead of believing in the myths
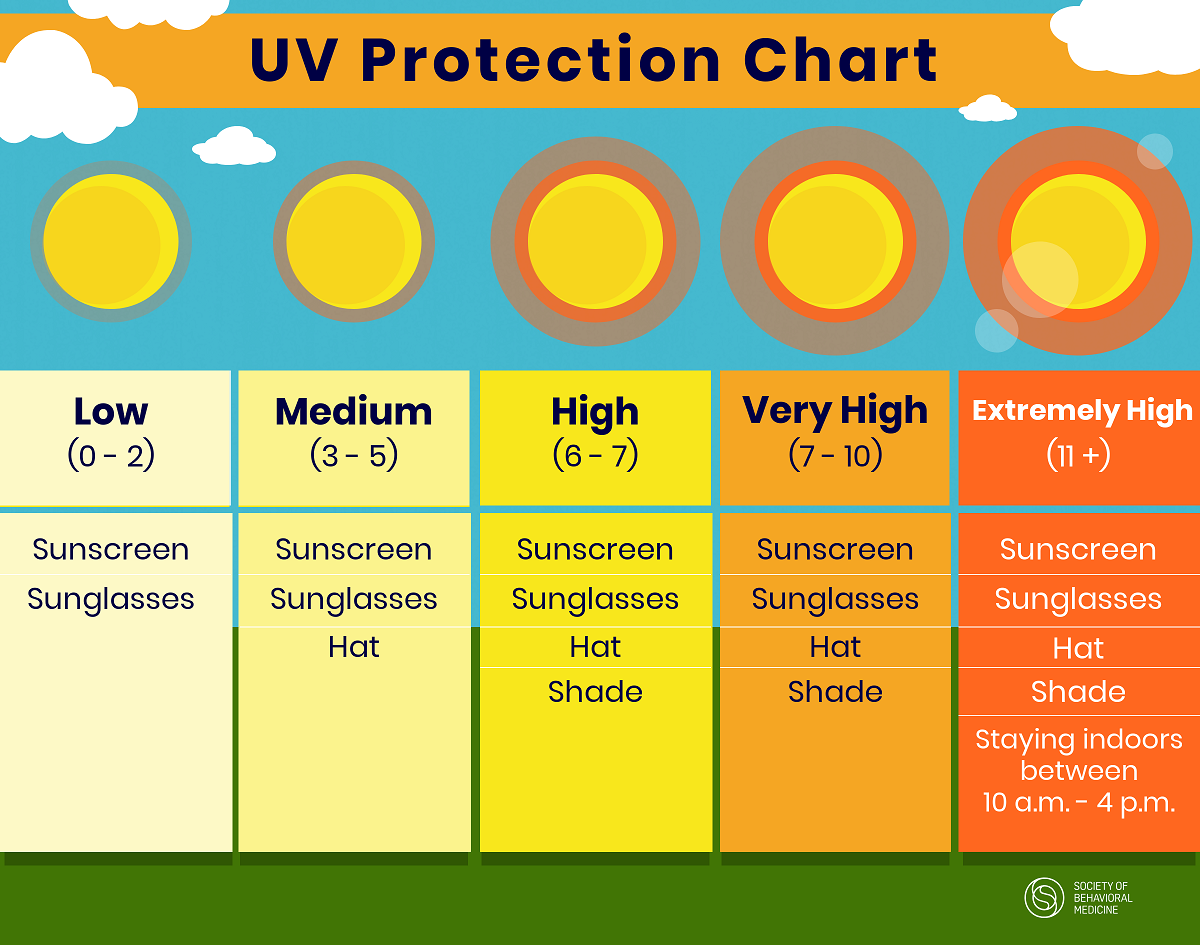
about sunscreen; instead, apply sunscreen before you step outside. Remember
that no sunscreen is perfect as well. Wear wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, or
other protective clothing, and seek shade whenever possible. Enjoy the warm,
friendly weather sensibly and healthily.
Photo: https://www.sbm.org/healthy-living/sun-safety-protect-your-skin-this-summer-and-all-year-round