Traditional Medicine: The Dual Face of Healing
Like any other traditional medicine, traditional African medicine has a rich history, deeply rooted in the continent's cultural and spiritual fabric. It offers numerous benefits, yet it also harbours significant dangers, mainly when exploited by unscrupulous practitioners.
Traditional African medicine is holistic, treating the mind, body, and spirit. The knowledge is often passed down through generations, harnessing the power of nature to cure various ailments.
Traditional African medicine's accessibility and affordability are key advantages. It is often more accessible and affordable than conventional Western medicine, particularly in rural areas with sparse modern healthcare facilities. Herbal remedies can be found locally, making them an immediate resource for those in need. This accessibility offers hope for improved healthcare in underserved communities.
Traditional African medicine is deeply embedded in the cultural context of African communities, making it culturally relevant and creating a sense of trust amongst Africans, especially those in the local community. This cultural relevance is a testament to the rich history and deep roots of traditional African medicine, which explains its holistic approach to treatment.
Traditional medicine's unique holistic approach to health, addressing physical symptoms and emotional and spiritual well-being, leads to more comprehensive and personalized care. This approach values the individual's well-being, making them feel cared for and valued.
Because traditional medicine healers have extensive knowledge of conventional medicines, they use natural ingredients such as herbs, roots, and plants to heal. The advantage of using natural ingredients is that the treatment typically has fewer side effects than synthetic drugs. Many modern pharmaceuticals are derived from these natural sources, indicating their potential and safety.
Risks
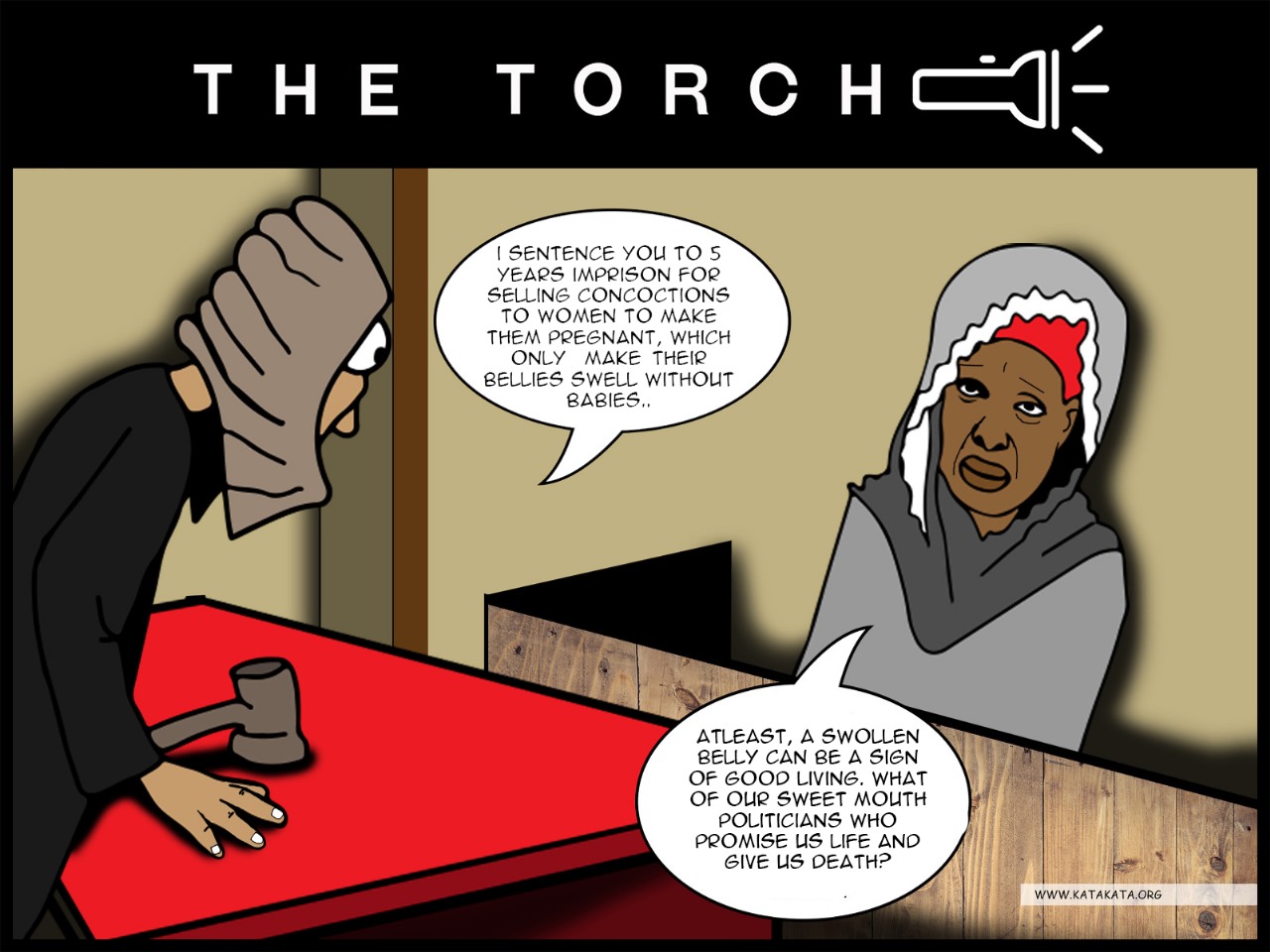
Despite its benefits, traditional medicine can pose significant dangers, significantly when misused or misrepresented by fraudulent healers. The comic portrays a fake healer who deceives women into believing they are receiving fertility treatment, only for the concoction to cause their bellies to swell without achieving the desired effect. Such a reality is not uncommon in traditional medicine.
Traditional medicines are often based on anecdotal evidence and need more rigorous scientific validation. This lack of scientific validation, which hardly follows proper research and testing, means that medicines need help ensuring their safety and efficacy. The unscientific approach can lead to the use of ineffective or harmful treatments.
Some unscrupulous traditional healers, often referred to as 'quack healers ', use potentially harmful ingredients such as conventional concoctions, which may contain toxic substances or contaminants that can cause adverse health effects. Without standardized dosages and quality control, the risk of poisoning or severe reactions increases. The risk of using fake and dangerous concoctions becomes even more hazardous when patients, primarily locals, are susceptible.
Patients' gullibility can be exploited by unscrupulous individuals posing as healers. These fake practitioners capitalize on the desperation of people seeking cures for severe conditions, offering false hope and ineffective treatments. The exploitations not only lead to financial loss and delays in receiving proper medical care, but they also expose patients' lives to danger.
The danger becomes aggravated when traditional remedies interact negatively with conventional medicines, which may lead to reduced efficacy or increased toxicity. Patients who do not disclose their use of traditional medicine to healthcare providers may face serious health risks due to these interactions.
Given the dangers associated with traditional medicine, the obvious question is: What is the way forward? A balanced approach is necessary to harness the benefits of traditional medicine while mitigating its dangers. This balanced approach could involve integrating traditional medicine with modern healthcare. The integration could include training traditional healers on basic medical principles and encouraging collaboration with conventional healthcare providers.
The government should play a crucial role in encouraging more research and standardization of traditional medicine. More research is needed to scientifically validate traditional remedies' efficacy and safety. Standardizing doses and ensuring quality control can help mitigate the risks associated with traditional medicine. The government can provide funding and support for such research and establish regulatory standards for the production and use of traditional remedies.
Educating the public and creating awareness about traditional medicine's potential risks and benefits is equally necessary. We can do this by encouraging patients to seek reputable practitioners and to discuss their use of traditional remedies with their healthcare providers.
Regulation and oversight implementation will help governments oversee traditional medicine practice, ensuring that practitioners are qualified and their treatments are safe and effective. They will also help protect patients from fraudulent healers.
Despite the dangers associated with traditional African medicine, mainly when exploited by quack healers, it holds immense potential for improving healthcare, especially in underserved communities. This potential offers hope and optimism for a more effective and safe healthcare system that respects cultural practices while safeguarding public health.